주메뉴
- About IBS 연구원소개
-
Research Centers
연구단소개
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe (Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe (Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Dark Matter Axion Group
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Center for Relativistic Laser Science
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (Neuro Technology Group)
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience Group)
- Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis
- Center for Genome Engineering
- Center for Nanomedicine
- Center for Biomolecular and Cellular Structure
- Center for 2D Quantum Heterostructures
- Center for Quantum Conversion Research
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center 뉴스 센터
- Career 인재초빙
- Living in Korea IBS School-UST
- IBS School 윤리경영


주메뉴
- About IBS
-
Research Centers
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe (Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe (Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Dark Matter Axion Group
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Center for Relativistic Laser Science
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (Neuro Technology Group)
- Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research (Cognitive and Computational Neuroscience Group)
- Center for Algorithmic and Robotized Synthesis
- Center for Genome Engineering
- Center for Nanomedicine
- Center for Biomolecular and Cellular Structure
- Center for 2D Quantum Heterostructures
- Center for Quantum Conversion Research
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center
- Career
- Living in Korea
- IBS School
News Center
Quantum Sensor for the Atomic World Developed through International Scientific Collaboration- “You have to be small to see small” - In a scientific breakthrough, an international research team from Korea's IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) and Germany's Forschungszentrum Jülich developed a quantum sensor capable of detecting minute magnetic fields at the atomic length scale. This pioneering work realizes a long-held dream of scientists: an MRI-like tool for quantum materials. The research team utilized the expertise of bottom-up single-molecule fabrication from the Jülich group while conducting experiments at QNS, utilizing the Korean team’s leading-edge instrumentation and methodological know-how to develop the world's first quantum sensor for the atomic world. The diameter of an atom is a million times smaller than the thickest human hair. This makes it extremely challenging to visualize and precisely measure physical quantities like electric and magnetic fields emerging from atoms. To sense such weak fields from a single atom, the observing tool must be highly sensitive and as small as the atoms themselves. A quantum sensor is a technology that uses quantum mechanical phenomena such as the spin of an electron or the entanglement of quantum states for precise measurements. Several types of quantum sensors have been developed over the past years. While many quantum sensors are able to sense electric and magnetic fields, it was believed that atomic-scale spatial resolution cannot be mastered simultaneously. The success of the new atomic-scale quantum sensor lies in the use of one single molecule. This is a conceptionally different way of sensing since the function of most other sensors relies on a defect – an imperfection – of a crystal lattice. Since such defects develop their properties only when they are deeply embedded into the material, the defect – capable of sensing electric and magnetic fields, will always remain at a rather large distance from the object preventing it from seeing the actual object on the scale of single atoms. The research team changed the approach and developed a tool that uses a single molecule to sense the electric and magnetic properties of atoms. The molecule is attached to the tip of the scanning tunneling microscope and can be brought within a few atomic distances of the actual object. Dr. Taner ESAT, the lead author of the Jülich team, expressed his excitement about the potential applications, stating, "This quantum sensor is a game changer because it provides images of materials as rich as an MRI and at the same time sets a new standard for spatial resolution in quantum sensors. This will allow us to explore and understand materials at their most fundamental level." The long-term collaboration hinged on Dr. Esat, previously a postdoc at QNS, who moved back to Jülich where he conceived of this sensing molecule. He chose to return to QNS for a research stay in order to prove this technique using the center's cutting-edge instruments. The sensor has an energy resolution that allows for detecting changes in magnetic and electric fields with a spatial resolution on the order of a tenth of an angstrom, where 1 Ångström typically corresponds to one atomic diameter. Moreover, the quantum sensor can be constructed and implemented in existing laboratories worldwide. "What makes this achievement so striking is that we use an exquisitely engineered quantum object to resolve fundamental atomic properties from the bottom up. Preceding techniques for visualizing materials use large, bulky probes to try to analyze tiny atomic features," stresses QNS’s lead author Dr. Dimitry BORODIN. "You have to be small to see small." This groundbreaking quantum sensor is poised to open up transformative avenues for engineering quantum materials and devices, designing new catalysts, and exploring the fundamental quantum behavior of molecular systems, such as in biochemistry. As BAE Yujeong, QNS’s PI for the project, noted, "The revolution in tools for observing and studying matter emerges from the accumulated basic science. As Richard FEYNMAN said, 'There's plenty of room at the bottom,' the potential of technology for manipulating at the atomic level is infinite." Professor Temirov, research group leader in Jülich, adds: “It is exciting to see how our long-standing work in molecular manipulation has resulted in the construction of a record-holding quantum device.” The research results were published in Nature Nanotechnology on July 25th. The development of this atomic-scale quantum sensor marks a significant milestone in the field of quantum technology and is expected to have far-reaching implications across various scientific disciplines. The results of the study were published online in the journal "Nature Communications" (IF=14.7) on July 11.
Video 1. Operating Principle of the Quantum Sensor Notes for editors
- References
- Media Contact
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
|
| Next | |
|---|---|
| before |
- Content Manager
- Public Relations Team : Yim Ji Yeob 042-878-8173
- Last Update 2023-11-28 14:20










 Figure 1. Unparalleled Performance of the Quantum Sensor
Figure 1. Unparalleled Performance of the Quantum Sensor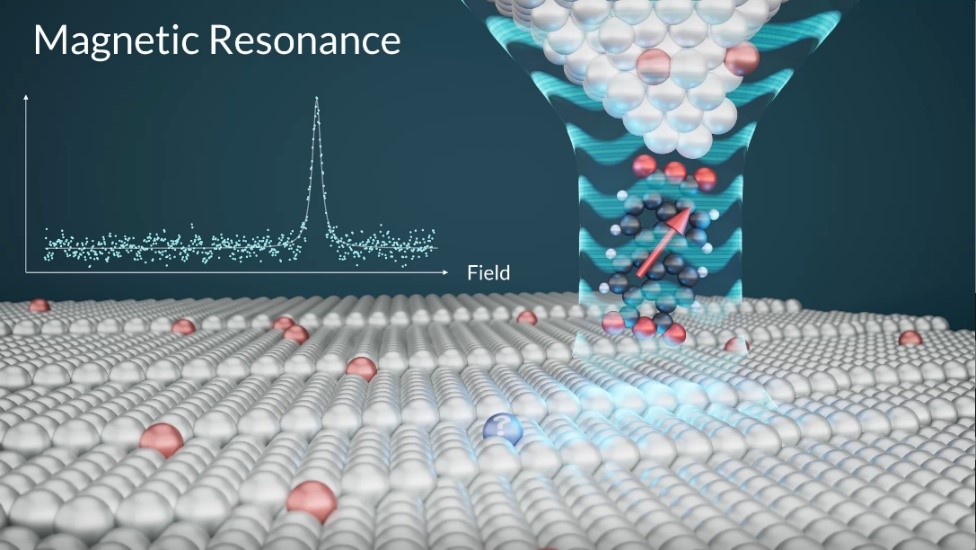 Figure 2. Operating Principle of the Quantum Sensor
Figure 2. Operating Principle of the Quantum Sensor
