주메뉴
- About IBS 연구원소개
-
Research Centers
연구단소개
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center 뉴스 센터
- Career 인재초빙
- Living in Korea IBS School-UST
- IBS School 윤리경영


주메뉴
- About IBS
-
Research Centers
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center
- Career
- Living in Korea
- IBS School
News Center
|
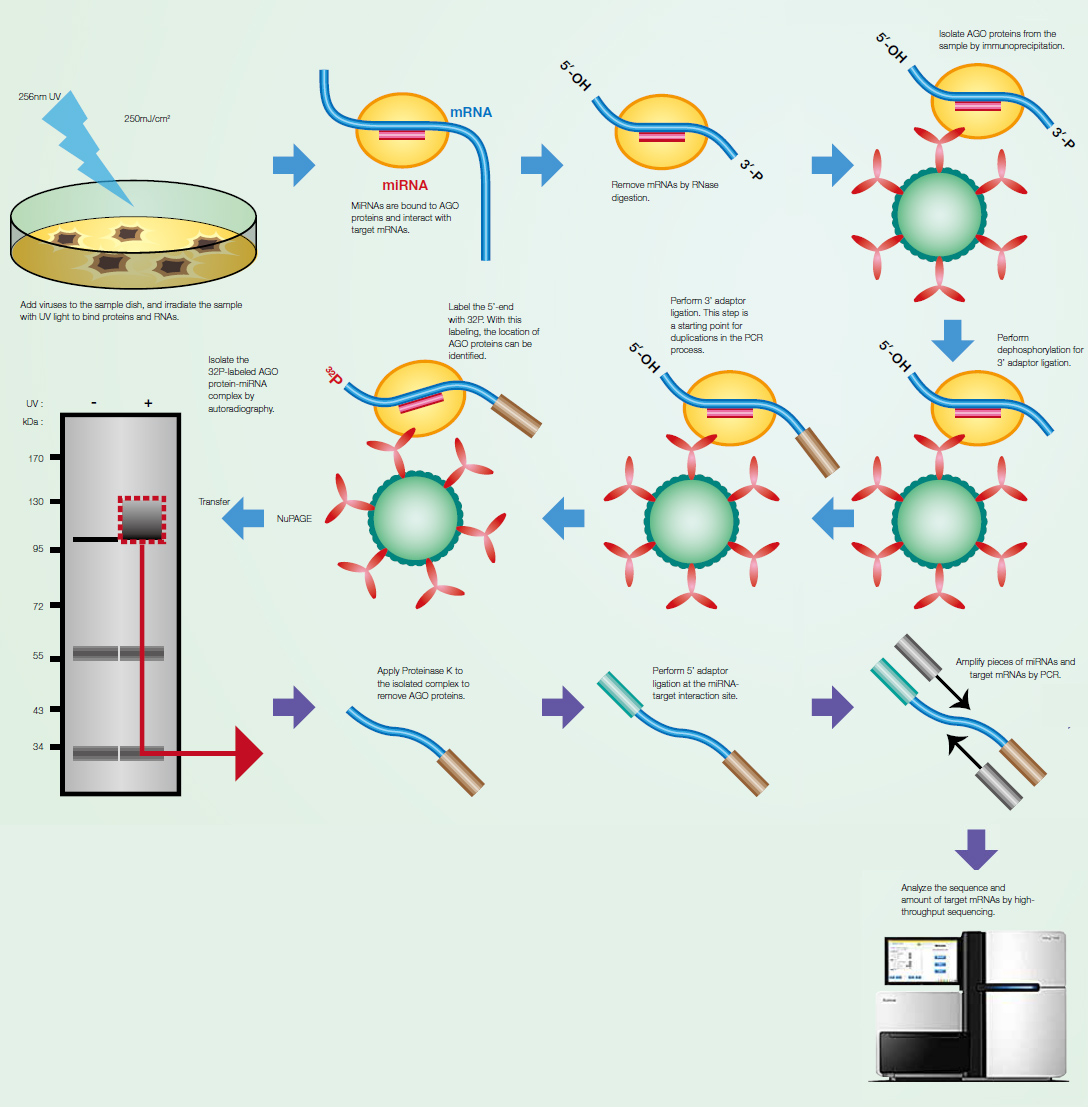
AGO-CLIP-Seq to identify vira miRNA targetomes MicroRNA (miRNA) is short non-coding RNA with
approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which plays a
post-transcriptional regulatory role in gene expression.
Published paper |
| before | |
|---|---|
| Next |
- Content Manager
- Public Relations Team : Suh, William Insang 042-878-8137
- Last Update 2023-11-28 14:20