주메뉴
- About IBS 연구원소개
-
Research Centers
연구단소개
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center 뉴스 센터
- Career 인재초빙
- Living in Korea IBS School-UST
- IBS School 윤리경영


주메뉴
- About IBS
-
Research Centers
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center
- Career
- Living in Korea
- IBS School
News Center
IBS Breakthrough in the Treatment of Cancer- Research Team from the IBS Center of Genome Integrity reports an inhibition of colon tumors in mice models - Scientists from the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have successfully inhibited the growth of colon tumors in mice with mismatch repair deficiency. The research team, headed by the Center’s director MYUNG Kyungjae, made the announcement in a manuscript published in the American Association for Cancer Research on June 6th. It is a significant breakthrough for the future treatment of colon cancer patients; specifically for those with DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficient tumors.
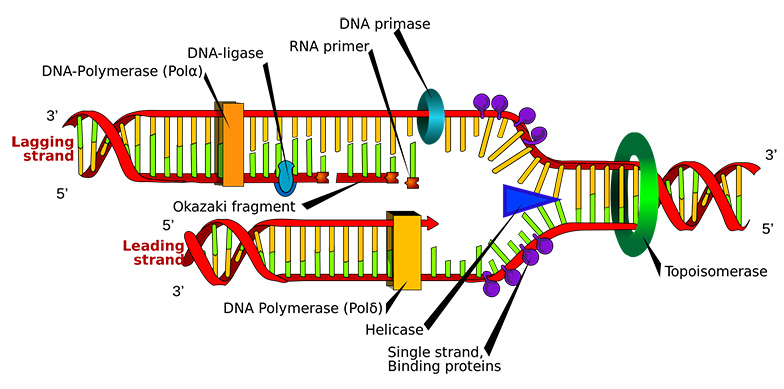
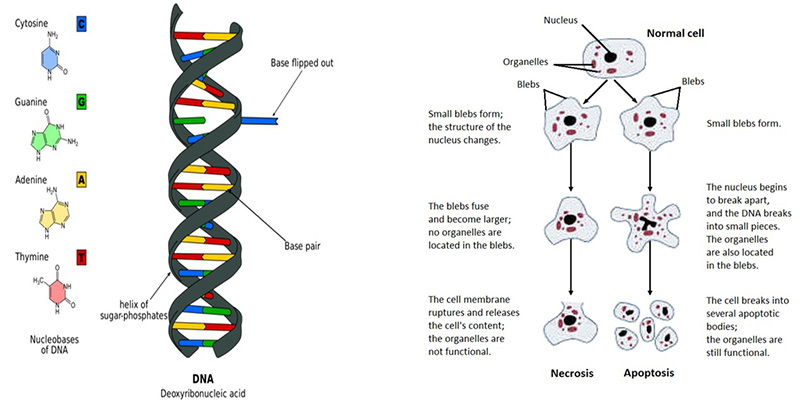
DNA Replication and Mismatch RepairDNA is intrinsic to all life on Earth. Every minute of every day our DNA is constantly evolving and susceptible to defects as individual DNA molecules are inherently unstable. DNA replication mistakes arise when DNA polymerase copies the two strands of DNA – the top and bottom strand. Generally there should be a balance between these strands: An ‘A’ opposite a ‘T’ and a ‘G’ opposite a ‘C’. However, mistakes can arise when the wrong nucleotide or base is replicated. For example a ‘T’ inserted in place of a ‘C’. This mistake should be repaired by DNA MMR but if this mechanism fails, the mutation has the potential to carcinogenesis. The cancer cells deficient in DNA MMR are resistant to most conventional chemotherapeutic drugs but the IBS team identified baicalein as a suitable antagonist to battle the malignant cancerous cells. Baicalein is a small molecule used as a herbal supplement to enhance liver health in some Asian counties. For the purposes of their research the team at IBS used the compound as it binds to mismatched DNA, effectively causing the cancerous cells to self-destruct in a tightly regulated cell suicide process known as apoptosis.
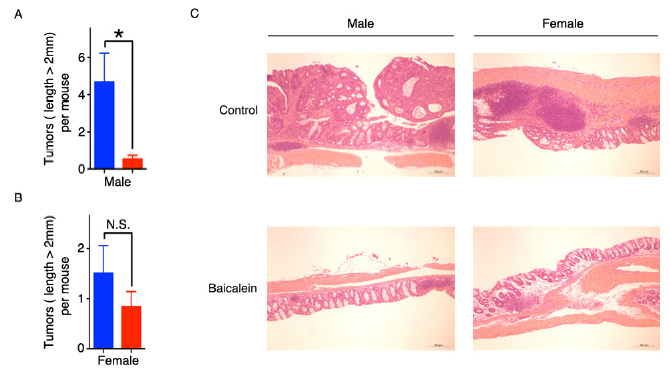
Reducing tumors in mice modelsTwo distinct mice models were used to test the team’s hypothesis: A controlled group composed of mice fed a global 18% protein rodent diet and an experimental group fed the same diet, but their 18% included 0.05% baicalein. MutSα is a protein complex that functions in DNA mismatch repair to block carcinogenesis. CHEK2 is a tumor suppressor which encodes CHK2, a protein that operates an intricate network of proteins. Their job is to elicit DNA repair, cell cycle arrest (DNA replication) or apoptosis in response to DNA damage. MutSα-deficient cancer cells are particular malignant and unresponsive to radiation or other chemotherapeutic treatments. MutSα interacts with CHK2 which can prevent cell cycle arrest or DNA repair. Baicalein is used to prevent an interaction between MutSα and CHK2.
The mice models were induced with colon tumors and exposed to a constant dose of baicalein over a two week period. Apoptotic cell death increased two fold by baicalein in MutSα-deficient tumors. The team, according to their manuscript, wanted to assess the effect of baicalein on tumor size over the course of time so repeated the exercise over a number of weeks. Baicalein continued to significantly shrink the MutSα-deficient tumors. IBS Director MYUNG, speaking from his research lab in Ulsan, South Korea, was obviously ecstatic at the results his team gleaned: “This research finding has great potential to target cancer therapy for patients who are diagnosed with mismatch repair deficient tumors. These particular types of tumors cover 10% of colon cancers.” The paper went on elucidate the finer points of baicalein as a future treatment for colon tumors: “A common critique of therapeutic strategies that target DNA repair deficiencies is that drugs that cause DNA damage often increase malignancy in the long term by inducing mutation rates. Baicalein, on the other hand, does not increase mutagenesis due to the ability of the DNA repair polymerase Polη to bypass baicalein-induced lesions in an error-free manner.” The research paper not only offers remarkable results but a viable option for an improved treatment option for patients with tumors with a DNA MMR deficiency. Neil Mannix Notes for editors - References - Media Contact - About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) |
|||
Center for Genomic Integrity |
|||
|
|
| Next | |
|---|---|
| before |
- Content Manager
- Public Relations Team : Suh, William Insang 042-878-8137
- Last Update 2023-11-28 14:20