주메뉴
- About IBS 연구원소개
-
Research Centers
연구단소개
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center 뉴스 센터
- Career 인재초빙
- Living in Korea IBS School-UST
- IBS School 윤리경영


주메뉴
- About IBS
-
Research Centers
- Research Outcomes
- Mathematics
- Physics
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Particle Theory and Cosmology Group)
- Center for Theoretical Physics of the Universe(Cosmology, Gravity and Astroparticle Physics Group)
- Center for Exotic Nuclear Studies
- Center for Artificial Low Dimensional Electronic Systems
- Center for Underground Physics
- Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research
- Center for Theoretical Physics of Complex Systems
- Center for Quantum Nanoscience
- Center for Van der Waals Quantum Solids
- Chemistry
- Life Sciences
- Earth Science
- Interdisciplinary
- Institutes
- Korea Virus Research Institute
- News Center
- Career
- Living in Korea
- IBS School
News Center
IBS Finds Another Aged Problem of How Naïve T Cells Decline with Age- Academy of Immunology & Microbiology (AIM) discovers the loss of naïve T cells is from deterioration in the environment that supports T cells - August 3, 2016 AIM, within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), published an intriguing paper in Scientific Reports, on August 2, detailing a novel explanation to a problem known to immunologists for decades: What causes the decline in immunity in old individuals? As soon as we are born we are destined to age, it’s a natural law which everyone adheres to. As we grow older our immunity gradually declines to a point where it is no longer able to effectively orchestrate an immune response to fight and extinguish pathogens. The flu vaccine, for example, is only 17 – 53% effective in people aged 60 and over, while this statistic surges to between 70 – 90% in younger people. T cells: Function and destinyT cells are essential for effective immunity and two broad types of cells exist to protect us: Naïve T cells and memory T cells. Naïve T cells are new recruits; they’ve neither fought nor been exposed to pathogens but are extremely diversified and provide essential cover against new infectious agents. Conversely, memory T cells are less diverse but are veterans; scarred and hardened from fighting malicious invaders. As soon as puberty begins naïve T cells start to gradually disappear, eventually rendering aged individuals more susceptible to infections, particularly from new pathogens that have not triggered memory cells. The prevailing view to explain the loss of naïve T cells is the decline in the production of new T cells in the thymus and a natural, life-long conversion of naïve T cells into memory cells. However, the thymus continues to produce low levels of naïve T cells as we age and T cells have a very long lifespan. So, what’s the real reason to explain the loss?
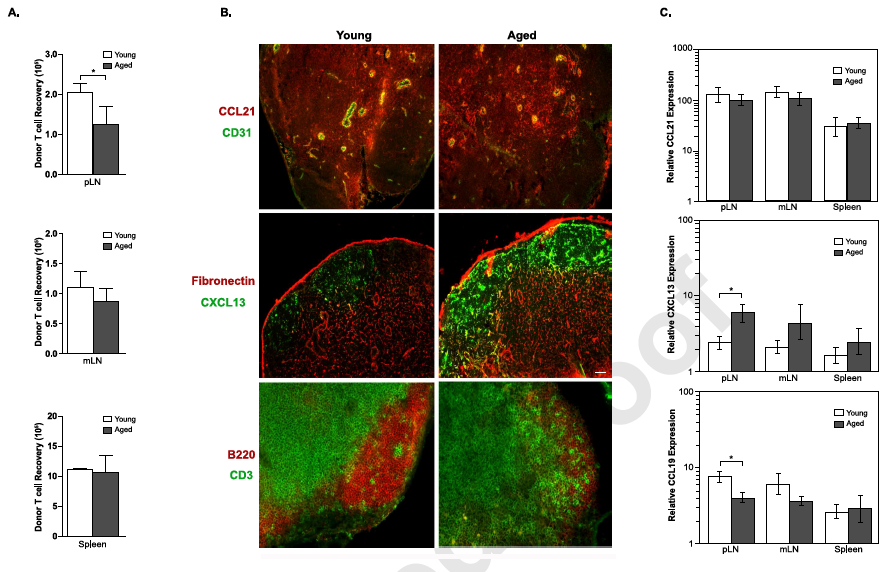
(A) Lymphocytes were isolated from B6.CD90.1+ Foxp3GFP+donor mice and 8.0 × 106 cells were injected into young (2 month) and aged (16 month) hosts. Bars show naïve donor T cell recovery in the pLN, mLN, and spleen of young and aged mice 4 hours after adoptive transfer. (B) Representative images are shown from young and aged pLN sections that were stained with the indicated antibodies and analyzed using immunofluorescence microscopy. Scale bars equal 50 μ m. (C) qPCR was used to determine the average normalized mRNA expression (± SD) of CCL21, CXCL13, and CCL19 in the pLN, mLN, and spleen of young and aged mice. An investigation into the loss of naïve T cellsCharles Surh, director of AIM, and his team have sought to answer this aged question. They looked at the lymph node and found deterioration in the population of stromal cells: Static cells that are essential in supporting the survival of naïve T cells while maintaining the structure of the lymph node. Director Surh explained, “This hypothesis had never been investigated before – to look whether a defect in the stromal cell population, within the lymph node contributed to naïve T cell loss. This defect must be rectified first before T cells can be replenished.” To investigate the legitimacy of their hypothesis the team set a number of experiments in place. Mice with lower than normal numbers of white blood cells {lymphopenic mice} were tested to see if they had the ability to support a natural proliferation of mature T cells. Previously, the team found this approach to be a sensitive way to measure the factors that support naïve T cell survival. Such factors declined moderately in middle-aged mice and sharply in old mice. The team also delivered extra naïve T cells into old mice, but to no avail. The injected T cells simply dissipated within two weeks in the old mice but persisted much longer in younger mice. The team’s hypothesis was looking promising. “It validated our informed suspicions that aging induces changes in the environment that supports T cell survival,” commented the amiable director. “Then, we focused our attention on the population of stromal cells in the lymph nodes.” To delve deep into the inner workings of naïve T cell survival it is paramount to study the subset of stromal cells in the lymph nodes that serve to support T cells, namely, the follicular reticular cells (FRCs). In essence the team found naïve T cells failed to effectively migrate into the lymph node and interact with FRCs. This was, according to the team’s paper, due to a decline in the production of a chemokine CCR19: A protein produced by endothelial and stromal cells to attract T cells to the lymph nodes to interact with FRCs. Moreover, the FRCs, which exist as a fine network of webbed structures in young mice, were found in lower numbers and highly disorganized in old mice.
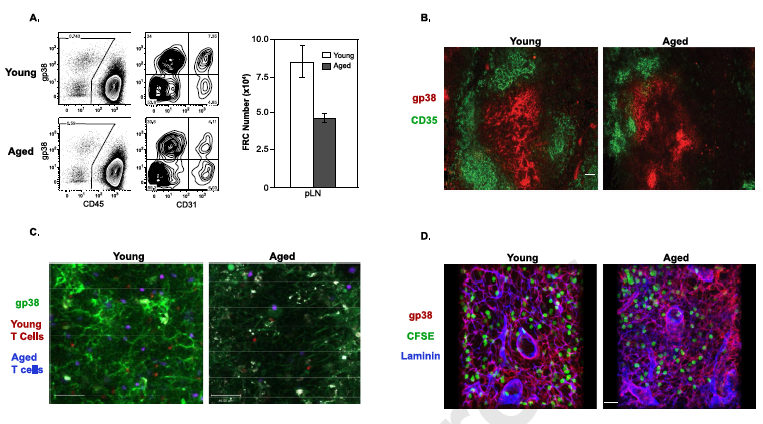
(A) LNs were removed from young and aged mice and FRCs were isolated by collagenase digestion. Plots show the gating strategy used to determine the total number of gp38+CD31−CD35− CD45− FRCs. Graph depicts the average number of FRCs recovered from the pLN of young and aged mice. (B) Representative images are shown from young and aged spleen sections stained with anti-gp38 and CD35 antibodies and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Scale bars equal 50 μm. (C) LN cells from young (2 month) or aged (20 month) mice were labeled with CMTPX (red) or CMTMR (blue), respectively, and 5.0 × 106 total cells were injected into age-matched littermate hosts. Hosts were injected with FITC-labeled anti-gp38 antibody 15–18 hours before analysis. Inguinal LN were explanted and visualized by multi-photon excitation microscopy. Images show representative data from 4 independent experiments and scale bars equal 50 μ m. (D) Naive T cells were labeled with CFSE and transferred into young and aged hosts. Representative images are shown from young and aged pLN vibratome sections stained with anti-gp38 and laminin antibodies analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. Scale bars are equal to 20 μ m. Problem solving at AIMThe results strongly supported the team’s theory. “Our work is the first to demonstrate that the decrease in naïve T cell numbers in old age is only not due to a decline in their {T cells} production in the thymus but also from deterioration in the environment that supports the survival of these cells,” said Director Surh, from AIM’s headquarters in Pohang, South Korea. “This is a new concept that has not been considered before, and could be a more relevant factor contributing to naïve T cell loss in old individuals than other previously suggested mechanisms. We hope that our contribution will trigger others to investigate why stromal cells that support naïve T cell survival deteriorate with age, as this will be a difficult question to solve on our own.” by Neil Mannix Notes for editors - References - Media Contact - About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) |
| Next | |
|---|---|
| before |
- Content Manager
- Public Relations Team : Suh, William Insang 042-878-8137
- Last Update 2023-11-28 14:20